Guide to Setting Up a Project Using a Compressed File
This guide will walk you through the process of setting up a project using a compressed file. Please follow the steps below carefully.
Make sure that the requirements.txt file is present in your project. If it is not available, you can create it using the command:
pip freeze > requirements.txt
If your application requires the installation of additional programs (such as ffmpeg or mysql-client), write the installation commands in the run.sh file and place this file in the root folder of your project.
Sample run.sh file:
#!/bin/bash
# ffmpeg (debian package)
sudo apt install -y ffmpeg
# mysql
sudo apt install -y gcc build-essential default-libmysqlclient-dev
Compressing the Project
To compress files on Linux operating systems, you can use the following command:
zip -r project.zip project_dir
Please ensure that your compressed file is in zip format and avoid using any other compression formats (such as rar, gz, 7z) for uploading to Kubar.
1. Initial Settings
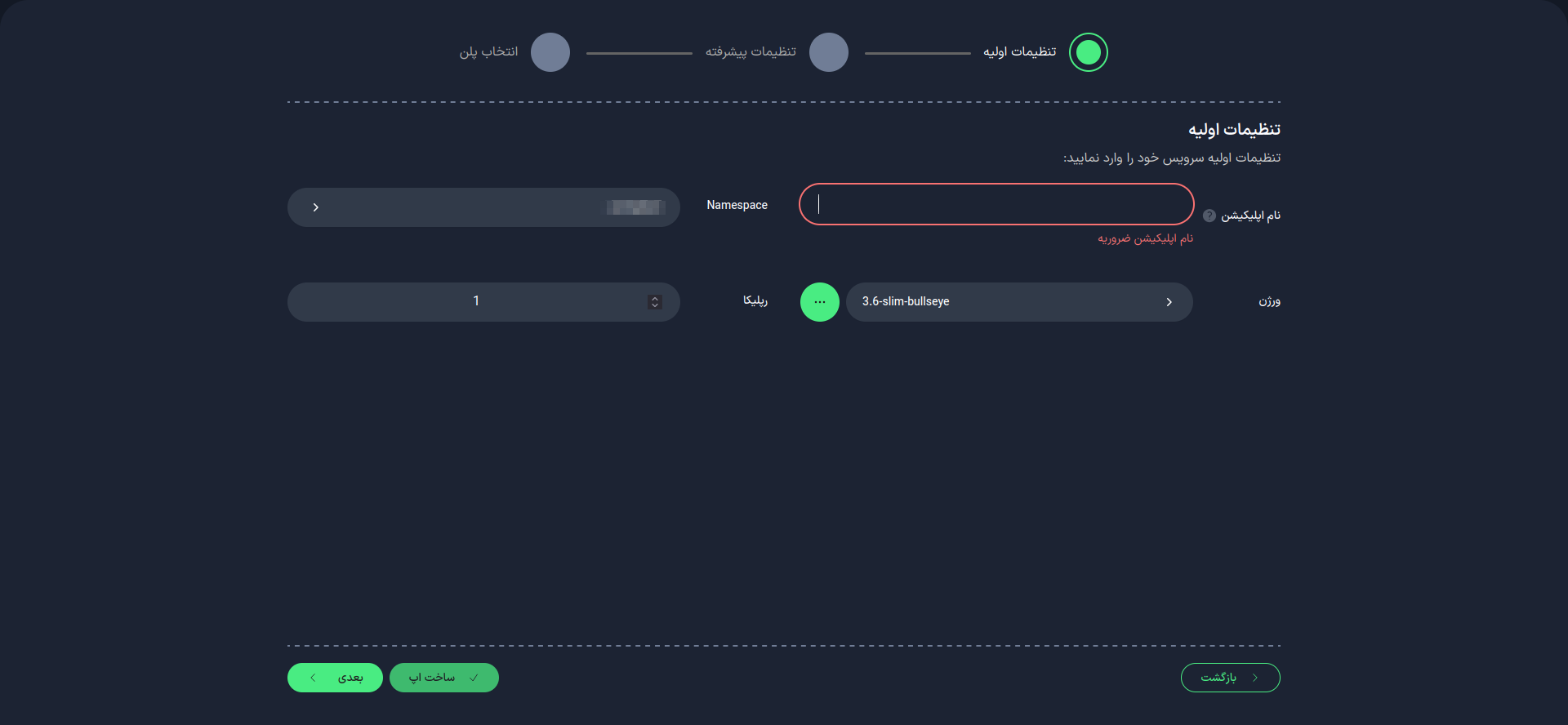
Application Name
First, choose a suitable name for your application. This name will be used as an identifier in your project domain.
- Use lowercase letters and only use - as a separator between words.
- The application name cannot be changed after the application is created.
Python Version
Select the Python version you will use for your project. You can choose from the available list or enter it manually. Please ensure that the Python version you are using is available in the Docker repository (Docker Hub) or other related Docker repositories.
After completing this step, select the "Next" option.
2. Advanced Settings (Optional)
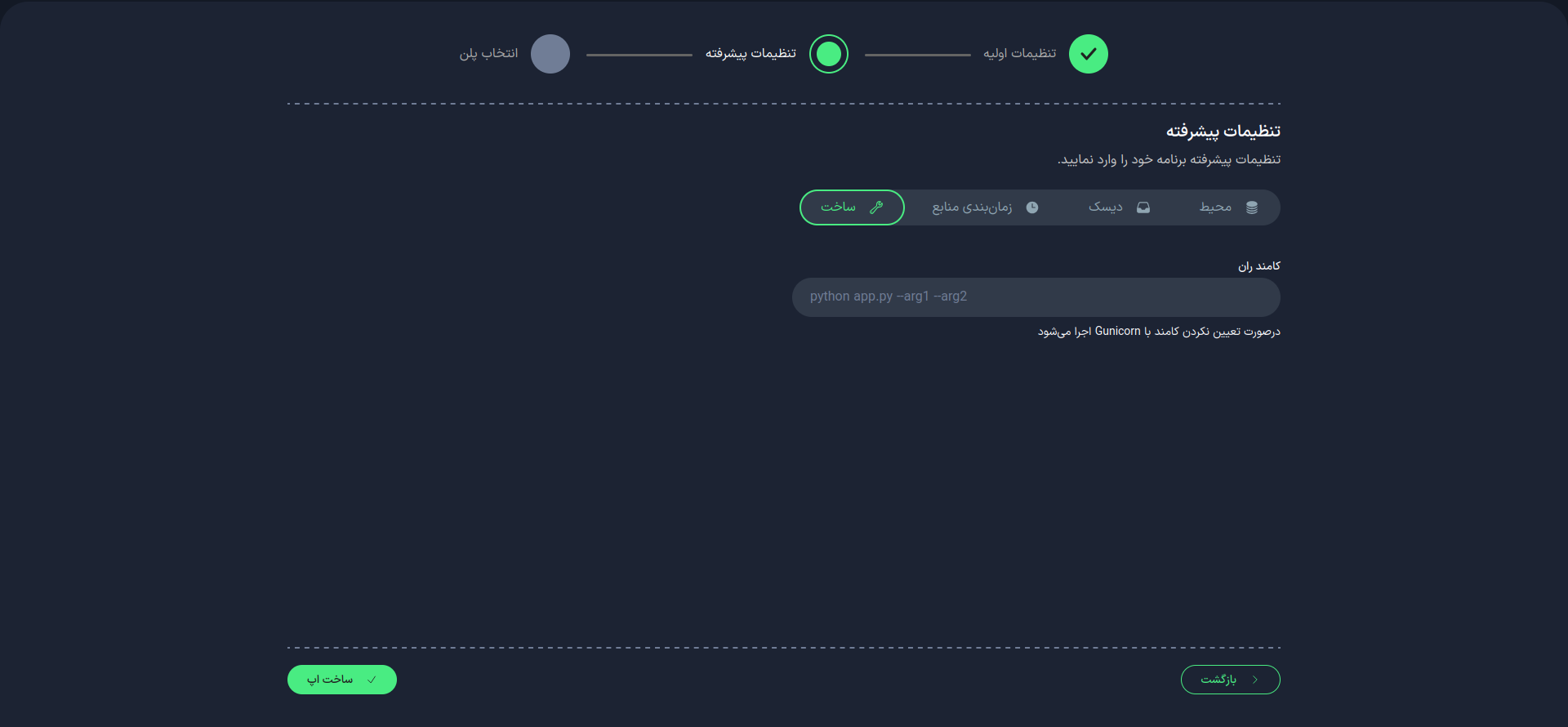
In this section, you can apply more advanced settings:
Build
Run Command
Kubar uses 'gunicorn' by default to run your application. If your application is not compatible with gunicorn or if you want to use a different command to run your service, you can enter it here.
Port
Specify the port number on which your application will run.
-
After the initial setup, changing the port is not possible.
-
If you entered a command in the command line, make sure your application listens on the address 0.0.0.0 and your desired port.
Resource Scheduling
Disk
Environment Variables
3. Select a Plan
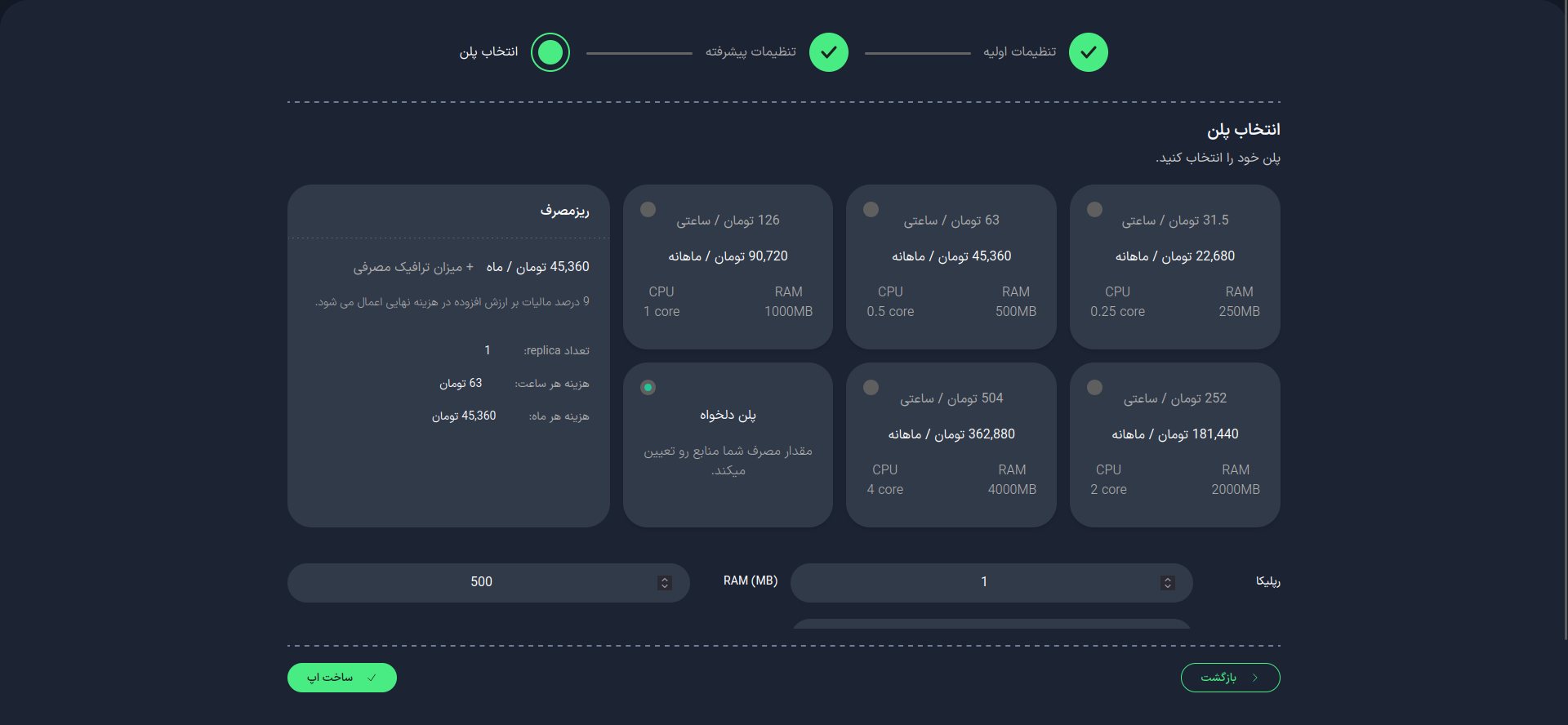
In this step, choose your desired plan. You can select from the available list or configure it manually.
Replicas
Specify the number of replicas (running instances) for your application. This number will affect the performance and availability of your application.
Importance of the Number of Replicas
- Scalability: Increased processing power with more replicas.
- High Availability: Maintaining performance in case one instance fails.
- Load Distribution: Distributing the load among multiple instances.
After selecting your desired plan, choose the Create App option.
4. Upload File
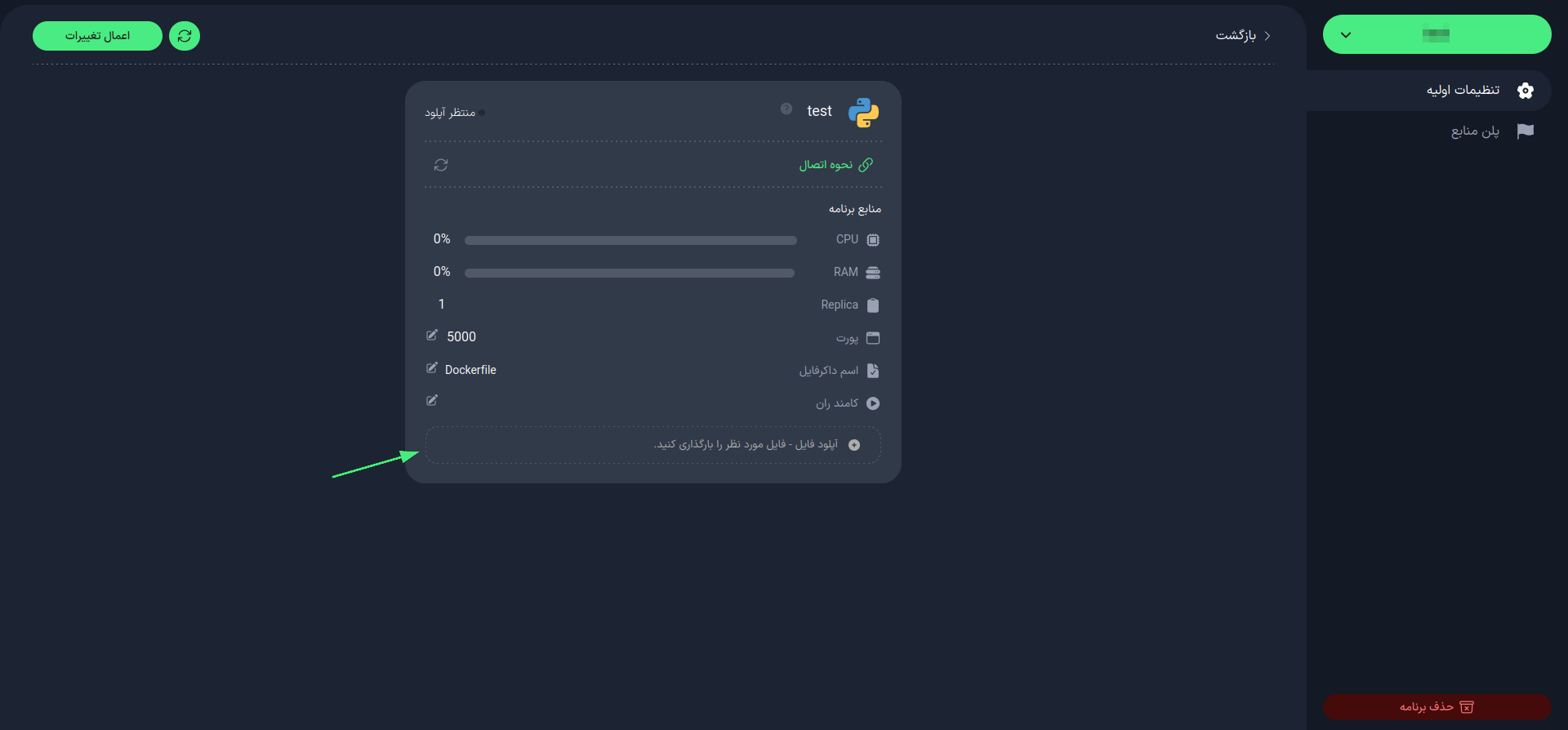
After creating your Python app, upload your compressed project file by clicking the "Upload File" button, and wait for the project to build.
5. Project Management
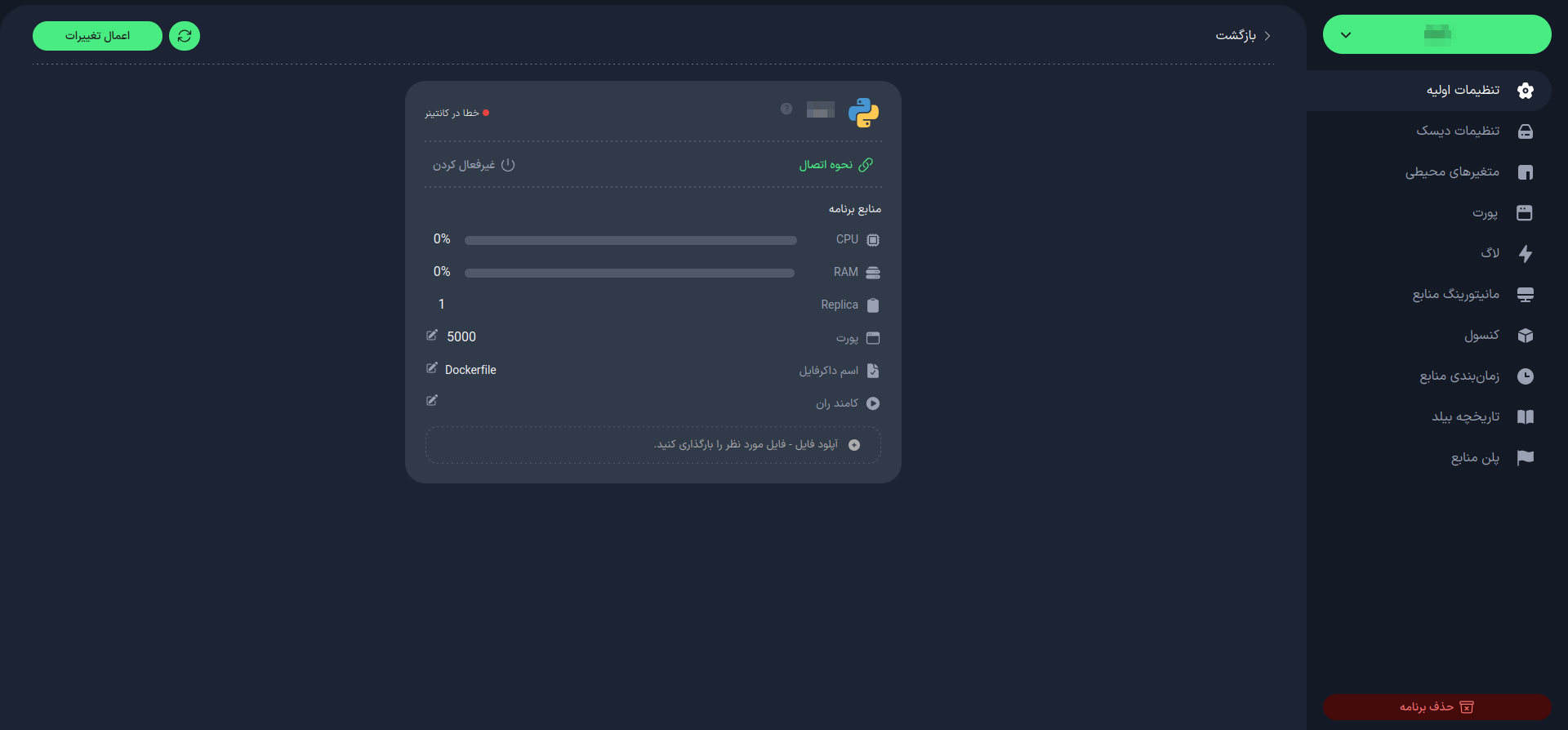
Once the project is built, you can manage your project from the "Project Management" section. In this section, you will have access to project management features:
-
Check project status
-
How to connect to the project
-
Review application resources
-
Number of replicas
-
Manage port
-
Rename Dockerfile (if needed)
tipIf your project requires very specific settings, you can create your own custom Dockerfile. For more information, refer to this link.
-
Change run command
-
Restart the project
With these features, you can effectively manage and maintain your project.