Application Port Management
The port management system on our platform allows developers to efficiently and securely configure and manage internal and external ports of their applications. This tool, by providing a simple and powerful user interface, helps you optimize network traffic routing and prevent potential conflicts. Our goal is to provide a seamless and secure experience in managing network communications for your applications.
What types of ports exist in applications?
Ports in applications are divided into two categories: internal and external:
- Internal Ports: These are ports used by the internal applications of our platform. They are used for internal communications between the various applications and services of the Kobar platform.
- External Ports: These are ports used for communications between your applications and other external applications and services, such as connecting to a database through your personal system.
How can I manage the ports of my applications?
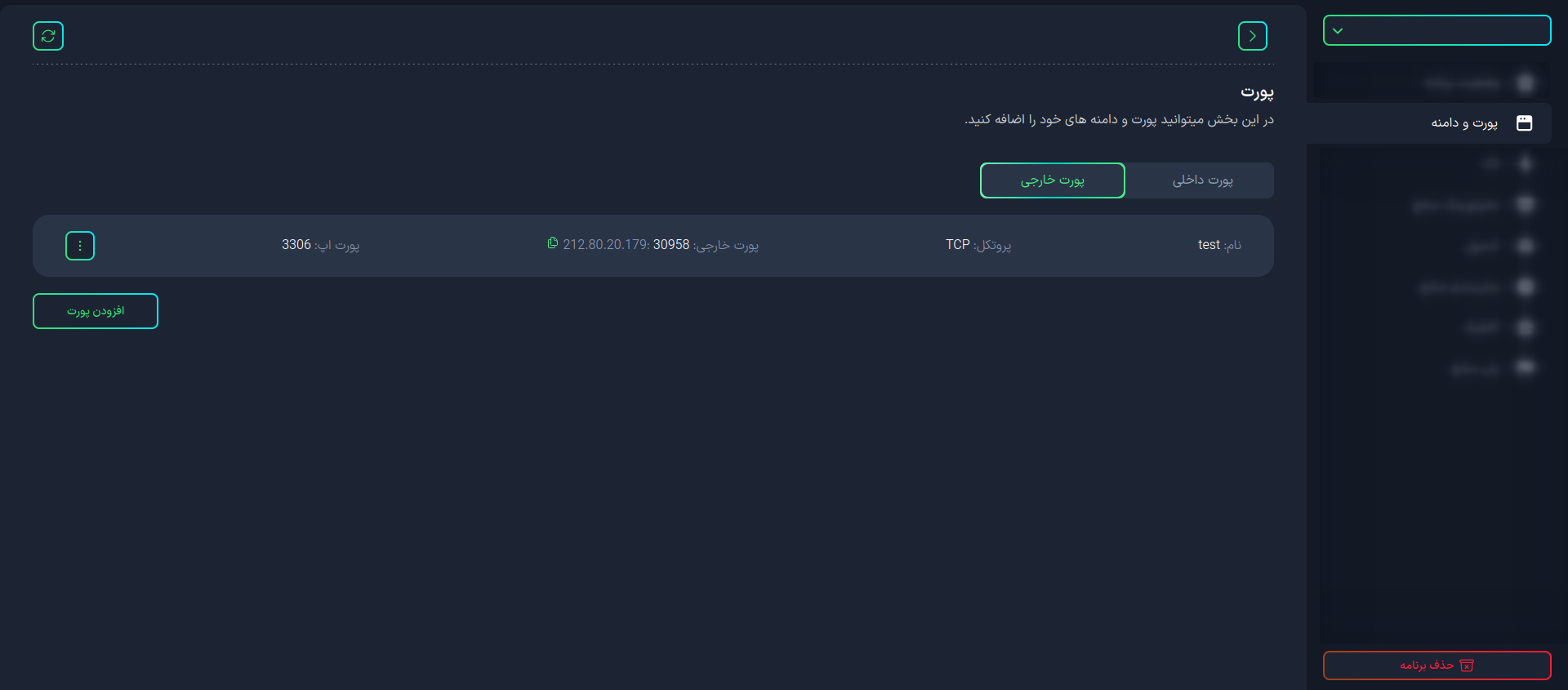
To access this tool, first log in to your application management panel. Then select the Ports and Domains tab.
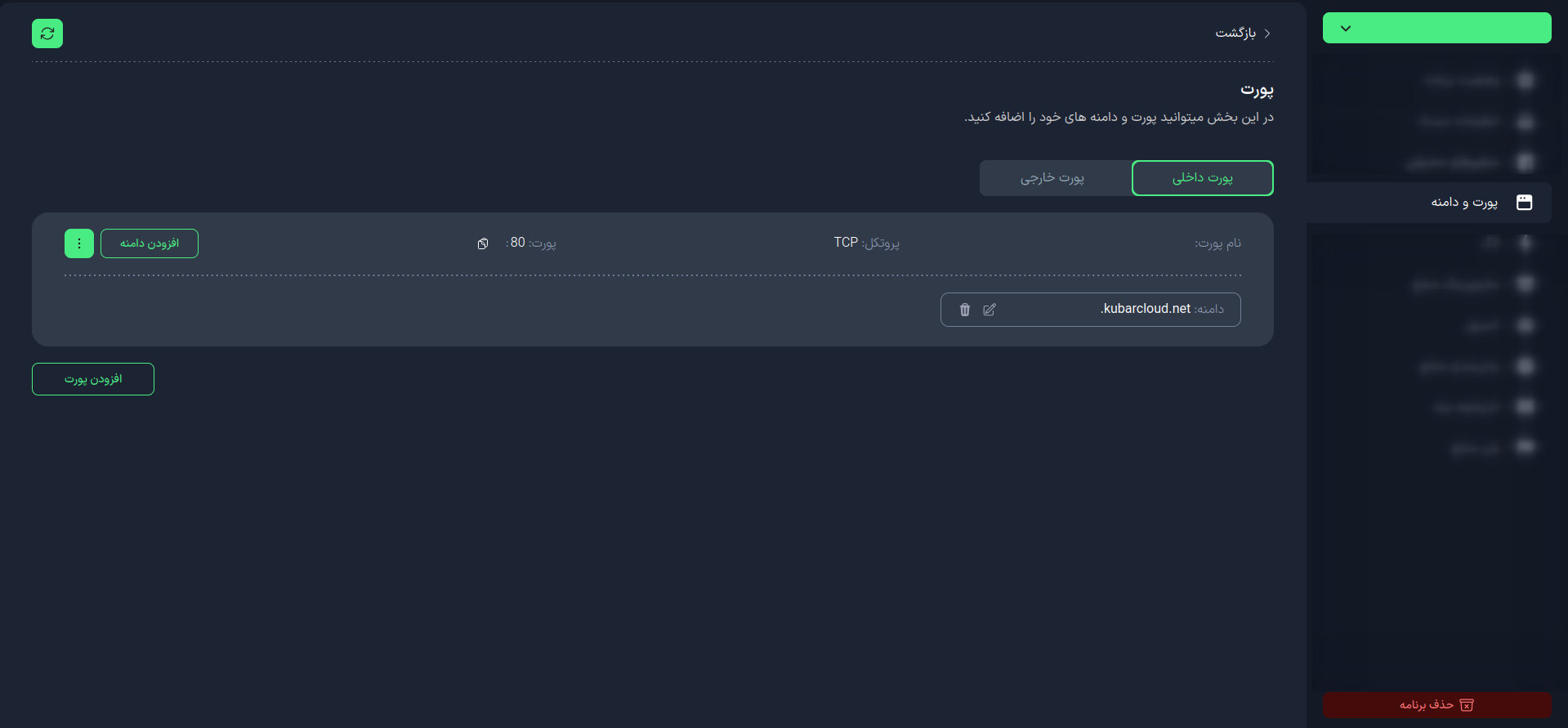
Once you enter this section, you can view and manage the internal and external ports of your applications.
- Internal Port
- External Port
After creating your application, the site assigns you an internal port. To add a new internal port, click the Add Port button in the Internal Port tab.
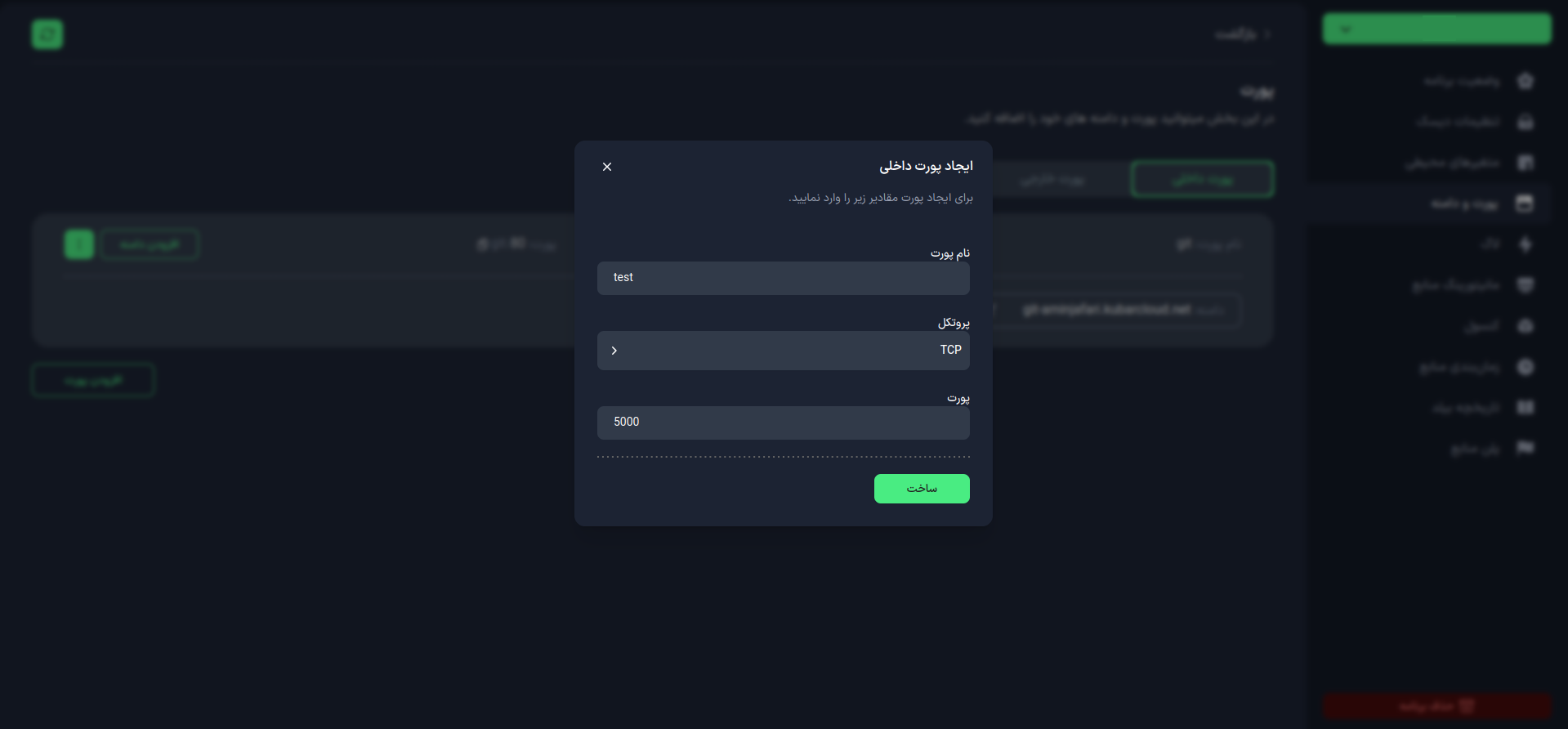
The features you can set for the internal port include:
- Port Name: The name used to identify the port.
- Protocol: The protocol used for port communications (such as TCP or UDP).
- Port: The destination port number for communications.
After completing the form, click the Create button to create the new internal port.
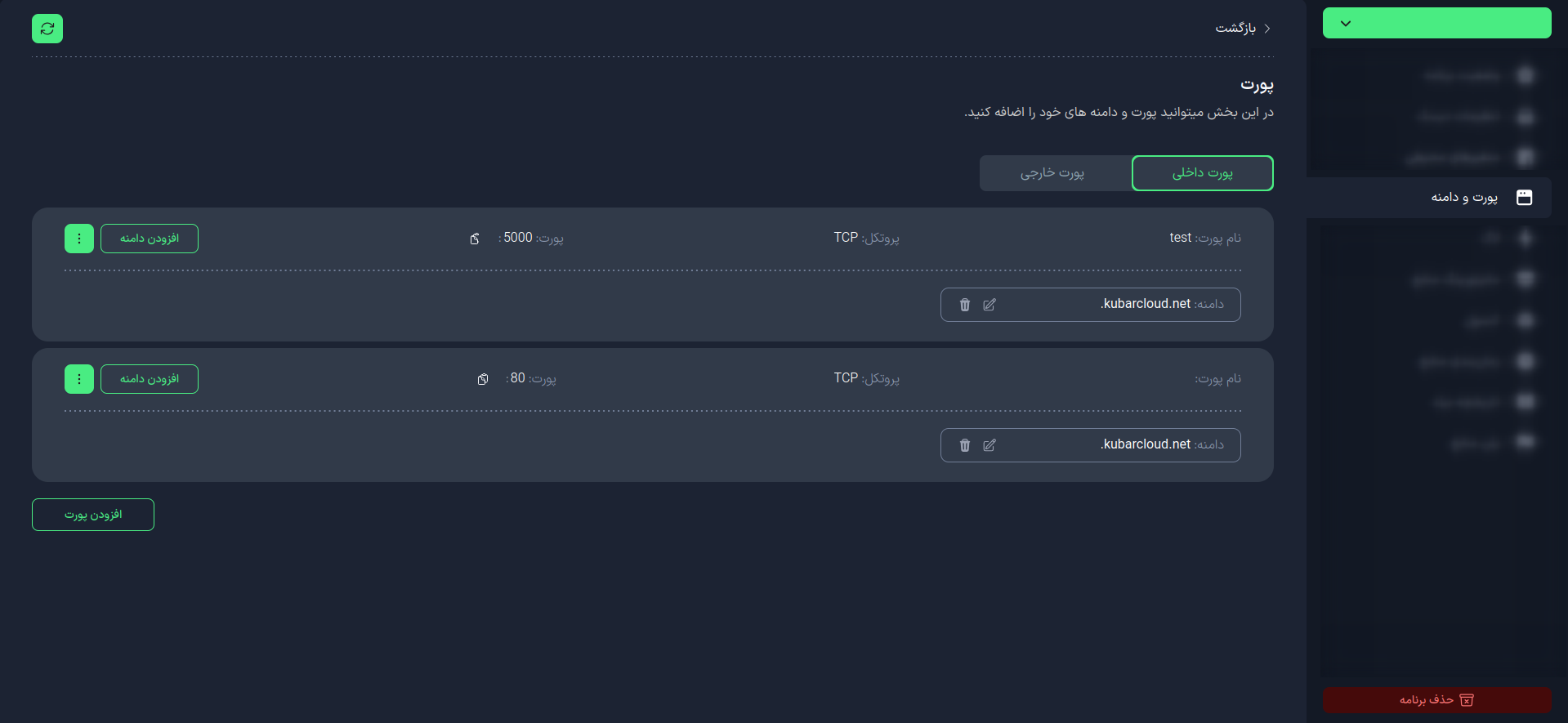
To add a new external port, click the Add Port button in the External Port tab.
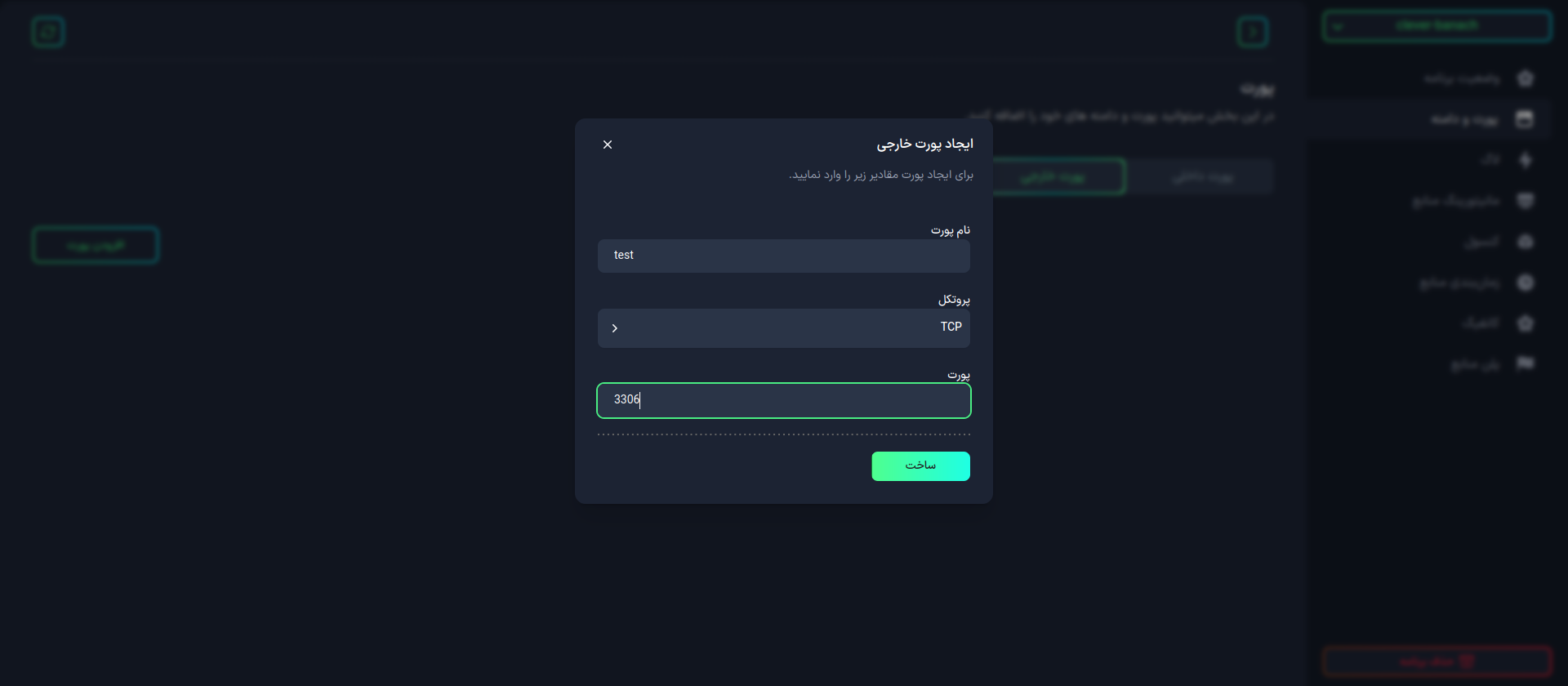
The features you can set for the external port include:
- Port Name: The name used to identify the port.
- Protocol: The protocol used for port communications (such as TCP or UDP).
- Port: The internal port number used for external communications.
After completing the form, click the Create button to create the new external port.
How can I delete a port?
To delete a port, click the button next to the desired port and select the Delete Port option.
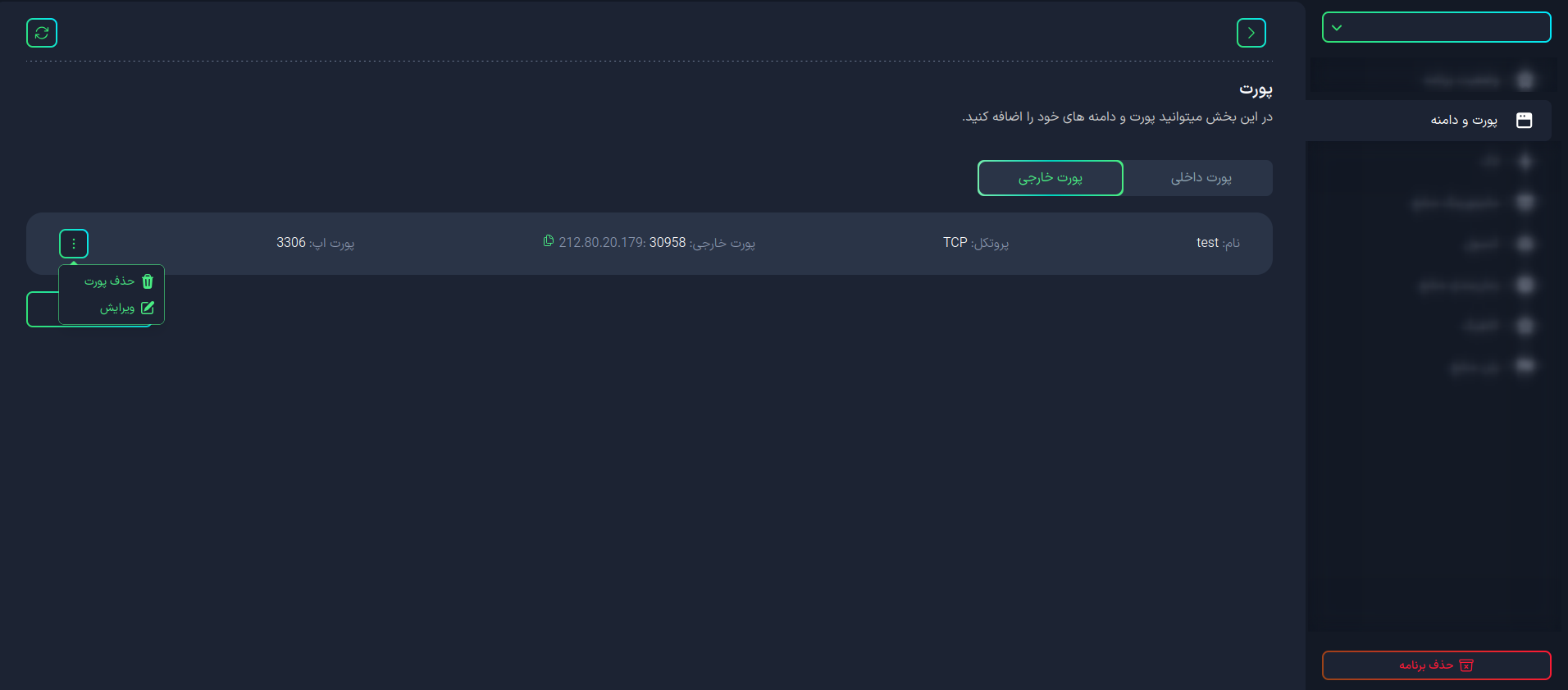
After confirmation, the selected port will be removed from the list of ports.
-
When creating an external port, ensure that the corresponding internal port exists.
-
The protocols used for port communications must be compatible with each other.